
Worked example: Look at the chromatogram in the diagram above.
Draw three conclusions about the three substances analysed by the chromatogram.
Answer: Any three from:
Substance A has four different substances, as there are four spots.
Substance B has three different substances, as there are three spots.
Substance C has three different substances, as there are three spots.
Substance A and B both have two of the same substances (red and pink spots).
Substances A and C both have two of the same substances (blue and yellow spots).
Substances B and C both have one of the same substances (green spot).
Worked example: Look at the chromatogram given here. Calculate the Rf value of the red spot.
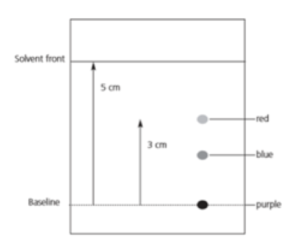
Answer: Rf value = distance travelled by the spot/ distance travelled by the solvent = ⅗ = 0.6
→What is Chromatography?Chromatography is a technique used to separate and identify the components of a mixture. It works by using the different physical and chemical properties of the components to separate them.
→What is the Rf value in Chromatography?The Rf value, also known as the retention factor, is a measure of the position of a component in a chromatographic separation. It is calculated by dividing the distance travelled by the component by the distance travelled by the solvent.
→Why is the Rf value important in Chromatography?The Rf value is important in Chromatography because it allows us to identify the components of a mixture. By comparing the Rf value of a component in a mixture to the Rf values of known compounds, we can determine the identity of the component.
→What factors can affect the Rf value of a component in Chromatography?The Rf value of a component in Chromatography can be affected by several factors, including the type of stationary phase, the polarity of the solvent, the temperature, and the concentration of the components in the mixture.
→How do you calculate the Rf value in Chromatography?To calculate the Rf value in Chromatography, you divide the distance travelled by the component by the distance travelled by the solvent. For example, if the component travels 5cm and the solvent travels 10cm, the Rf value is 0.5.
→How does Chromatography work?Chromatography works by using the different physical and chemical properties of the components in a mixture to separate them. The mixture is applied to a stationary phase, such as a piece of paper or a column, and a solvent is added. The components in the mixture move at different speeds through the stationary phase based on their properties, allowing them to be separated.
→What are the different types of Chromatography?There are several different types of Chromatography, including Paper Chromatography, Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC), Column Chromatography, and Gas Chromatography (GC). Each type uses a different stationary phase and a different method for separating the components of a mixture.
→How is Chromatography used in real-life applications?Chromatography is used in a variety of real-life applications, including the analysis of food and drink, the identification of drugs and chemicals, and the separation of proteins and enzymes in biochemistry. It is also used in environmental testing to detect and measure pollutants in air, water, and soil.